Today's Lesson: Integrating Circuits
What is it?
This is a lesson about integrating electronics into your 3D projects.Here are two circuits:
Circuit 1

Flickering Candle LED and Battery
Circuit 2
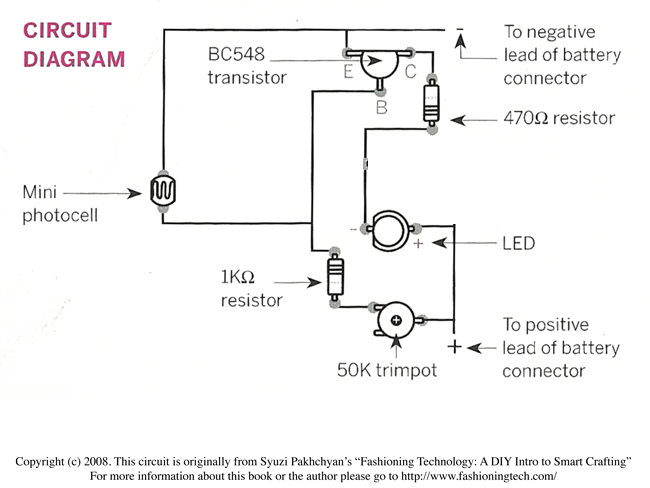
Materials and Tools
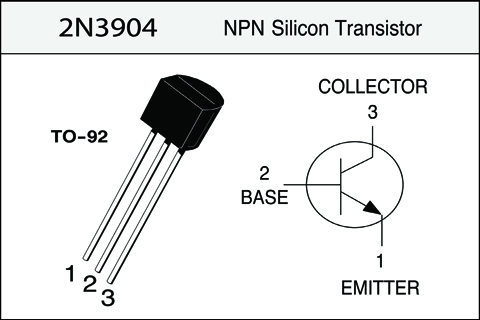
- BC548 or 2N2219 or 2N2906 transistor
- 470Ω resistor
- 1K Ω resistor
- yellow flickering candle LED
- 1 LDR
- 1 10K potentiometer
- 9V battery
- battery clip
Transistor Basics
Bipolar Transistors are composed of three layers:- An Input Layer, the emitter
- A Control Layer, the base
- An Output Layer, the collector
Layers are formed by doping silicon with traces of impurities. Silicon treated with Boron produces negative type material. It is negative because it has a surplus of electrons. Doping the silicon with Phosphorous produces positive material, or material with a surplus of electron holes.
Silicon transistors are considered semiconductors because they conduct only a small amount of current unless a change in voltage is applied at a juncture.
When current is applied to the input layer, or the emitter of an NPN transistor, electrons flow to the P-type base and fill the positive material, or electron holes. When the holes are filled, the material no longer conducts current. But when a small voltage is applied to the control layer, or base, that current will produce additional holes which in turn allows current to flow from the emitter through the base to the collector.
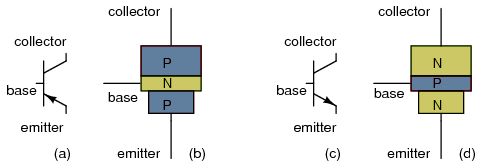
The difference between a PNP transistor and an NPN transistor is the polarity, or proper biasing of the junctions. Transistors restrict the amount of current passed according to a smaller, controlling current. The main current from collector to emitter (PNP) or from emitter to collector (NPN) depends on the type of transistor it is. The small current that controls the main current goes from base to emitter (PNP), or from emitter to base (NPN), depending on the kind of transistor it is.
The arrow always points against the direction of electron flow.
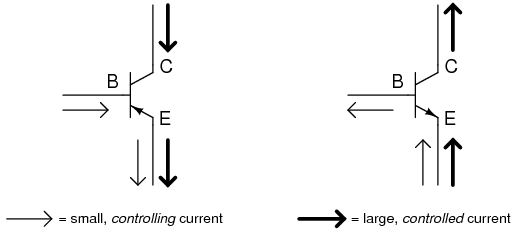
Bipolar transistors are called bipolar because the main flow of electrons through them takes place in two types of semiconductor material: P and N, as the main current goes from emitter to collector (or vice versa). Two types of charge carriers: electrons and holes, comprise the main current through the transistor.
All currents must be going in the proper directions for the device to work as a current regulator. The small, controlling current is usually referred to as the base current because it is the only current that goes through the base wire of the transistor.
The large, controlled current is referred to as the collector current because it is the only current that goes through the collector wire.
Switches
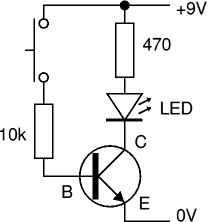
If there is no current through the base of the transistor, the transistor shuts off the controlled current like an open switch and prevents current through the collector. A base current, turns the transistor on like a closed switch and allows a proportional amount of current through the collector. Collector current is primarily limited by the base current, regardless of the amount of voltage available to push it.
Challenge
Pick one circuit. If you select the first, consider adding a switch. Figure out the space the circuit needs. Create a negative model for the circuit. Then create your positive and boolean difference the negative. Print!Document Your Project
What to include?- Sketches
- CAD files
- Goals
- Diagrams
Standards
from Next Generation Science Standards
| Next Generation Science | framework | |
| 1. | Asking questions and defining problems | √ |
| 5 | Using mathematics, information and computer technology, and computational thinking. | √ |
| 8 | Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information | √ |
| ETS-ED: Engineering Design | ||
| Defining and delimiting engineering problems involves stating the problem to be solved as clearly as possible in terms of criteria for success and constraints, or limits. | √ | |
| Designing solutions to engineering problems begins with generating a number of different possible solutions, evaluating potential solutions to see which ones best meet the criteria and constraints of the problem, then testing and revising the best designs. | √ | |
| Optimizing the design solution involves a process of tradeoffs, in which the final design is improved by trading off less important features for those that are more important. This may require a number of iterations before arriving at the best possible design. | √ | |
| ETS-ETSS: Engineering, Technology, Science and Society | ||
| Influence of engineering, technology, and science, on society and the natural world also involves two complementary ideas. The first is that scientific discoveries and technological decisions affect human society and the natural environment. The second is that people make decisions that guide the work of scientists and engineers. | √ | |
Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics
| Geometry | 6 | |
| Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume. | ||
| 1 | Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. | √ |
| 4 | Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. | √ |
| Geometry | 7 | |
| Draw construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. | ||
| 1 | Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. | √ | Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume. |
| 6 | Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and threedimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms. | √ |
| Geometry | 8 | |
| Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume of cylinders, cones, and spheres. | ||
| 9 | Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. | √ |
| Congruence | G-CO | |
| Experiment with transformations in the plane | ||
| 1 | Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. | √ |
| 4 | Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. | √ |
| Make geometric constructions | ||
| 12 | Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. | √ |
| Modeling with Geometry | G-MG | |
| Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations | ||
| 1 | Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder). | √ |
| 3 | Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios) | √ |
CDOS
- Standard 2: Integrated Learning
Students will demonstrate how academic knowledge and skills are applied in the workplace and other settings.
Integrated learning encourages students to use essential academic concepts, facts, and procedures in applications related to life skills and the world of work. This approach allows students to see the usefulness of the concepts that they are being asked to learn and to understand their potential application in the world of work.
Intermediate 2.2 Solve problems that call for applying academic knowledge and skills √
Commencement 2.1 Demonstrate the integration and application of academic and occupational skills in their school learning, work, and personal lives. √ 2.2 Use academic knowledge and skills in an occupational context, and demonstrate the application of these skills by using a variety of communication techniques (e.g., sign language, pictures, videos, reports, and technology) √ - Standard 3a: Universal Foundation Skills
Students will demonstrate mastery of the foundation skills and competencies essential for success in the workplace.
- Basic skills
Basic skills include the ability to read, write, listen, and speak as well as perform arithmetical and mathematical functions.
Elementary 3.1.1 Listen to and read the ideas of others and express themselves both orally and in writing; they use basic mathematical concepts and computations to solve problems. √
Intermediate 3.1.1 Listen to and read the ideas of others and analyze what they hear and read; acquire and use information from a variety of sources; and apply a combination of mathematical operations to solve problems in oral or written form. √
Commencement 3.1.1 Use a combination of techniques to read or listen to complex information and analyze what they hear or read; convey information confidently and coherently in written or oral form; and analyze and solve mathematical problems requiring use of multiple computational skills. √ - Thinking skills
Thinking skills lead to problem solving, experimenting, and focused observation and allow the application of knowledge to new and unfamiliar situations.
Elementary 3.2.1 Use ideas and information to make decisions and solve problems related to accomplishing a task. √
Intermediate 3.2.1 Evaluate facts, solve advanced problems, and make decisions by applying logic and reasoning skills. √
Commencement 3.2.1 Demonstrate the ability to organize and process information and apply skills in new ways. √
- Personal Qualities
Personal qualities generally include competence in self-management and the ability to plan, organize, and take independent action.
Elementary 3.3.1 Demonstrate the personal qualities that lead to responsible behavior. √
Intermediate 3.3.1 Demonstrate the ability to work with others, present facts that support arguments, listen to dissenting points of view, and reach a shared decision. √
Commencement 3.3.1 Demonstrate leadership skills in setting goals, monitoring progress, and improving their performance. √
- Interpersonal Skills
Positive interpersonal qualities lead to teamwork and cooperation in large and small groups in family, social, and work situations.
Intermediate 3.4.1 Demonstrate the ability to work with others, present facts that support arguments, listen to dissenting points of view, and reach a shared decision. √
Commencement 3.4.1 Communicate effectively and help others to learn a new skill. √
- Technology
Technology is the process and product of human skill and ingenuity in designing and creating things from available resources to satisfy personal and societal needs and wants.
Intermediate 3.5.1 Select and use appropriate technology to complete a task. √
Commencement 3.5.1 Apply their knowledge of technology to identify and solve problems. √
- Managing Information
Information management focuses on the ability to access and use information obtained from other people, community resources, and computer networks.Elementary 3.6.1 Describe the need for data and obtain data to make decisions. √
Intermediate 3.6.1 Select and communicate information in an appropriate format (e.g., oral, written, graphic, pictorial, multimedia). √
Commencement 3.6.1 Use technology to acquire, organize, and communicate information by entering, modifying, retrieving, and storing data. √
- Managing Resources
Using resources includes the application of financial and human factors, and the elements of time and materials to successfully carry out a planned activity.Elementary 3.7.1 Demonstrate an awareness of the knowledge, skills, abilities, and resources needed to complete a task. √
Intermediate 3.7.1 Understand the material, human, and financial resources needed to accomplish tasks and activities. √
Commencement 3.7.1 Allocate resources to complete a task. √
- Systems
Systems skills include the understanding of and ability to work within natural and constructed systems.Elementary 3.8.1 Demonstrate understanding of how a system operates and identify where to obtain information and resources within the system. √
Intermediate 3.8.1 Understand the process of evaluating and modifying systems within an organization. √
Commencement 3.8.1 Demonstrate an understanding of how systems performance relates to the goals, resources, and functions of an organization. √
- Basic skills
Career Development and Occupational Studies
Standards-based education addresses three types of standards
- content—identify what students should know and be able to do
- performance—identify levels of achievement in relation to the content standards, answering the question "How good is good enough?"
- opportunity-to-learn—the availability of resources, programs, and qualified teachers needed to enable the students to meet the identified standards.
| CDOS Standards | ||
| Learning experiences have real-life applications. | √ | |
| Lessons are authentic and project-based. | √ | |
| Lessons are experiential in nature. | √ | |
| Lessons are hands-on. | √ | |
| Students learn and then apply skills they learn in school. | √ | |
| Students integrate knowledge with experience. | √ | |
| Students offer comments of how much they are looking forward to their future careers because classroom activities are relevant to the real world. | √ | |
| Assessment directly measures performance. | √ | |
-
Standard 2:
Intermediate 2.2 Solve problems that call for applying academic knowledge and skills √ 2.3 Use academic knowledge and skills in an occupational context, and demonstrate the application of these skills by using a variety of communication techniques (e.g., sign language, pictures, videos, reports, and technology). √
Commencement 2.1 Demonstrate the integration and application of academic and occupational skills in their school learning, work, and personal lives. √ 2.2 Use academic knowledge and skills in an occupational context, and demonstrate the application of these skills by using a variety of communication techniques (e.g., sign language, pictures, videos, reports, and technology) √ - Standard 3a:
Universal Foundation Skills Students will demonstrate mastery of the foundation skills and competencies essential for success in the workplace.
- Basic skills
Basic skills include the ability to read, write, listen, and speak as well as perform arithmetical and mathematical functions.
Intermediate 3.1.1 Listen to and read the ideas of others and analyze what they hear and read; acquire and use information from a variety of sources; and apply a combination of mathematical operations to solve problems in oral or written form. √
Commencement 3.1.1 Use a combination of techniques to read or listen to complex information and analyze what they hear or read; convey information confidently and coherently in written or oral form; and analyze and solve mathematical problems requiring use of multiple computational skills. √ - Thinking skills
Thinking skills lead to problem solving, experimenting, and focused observation and allow the application of knowledge to new and unfamiliar situations.
Intermediate 3.2.1 Evaluate facts, solve advanced problems, and make decisions by applying logic and reasoning skills. √
Commencement 3.2.1 Demonstrate the ability to organize and process information and apply skills in new ways. √
- Personal Qualities
Personal qualities generally include competence in self-management and the ability to plan, organize, and take independent action.
Intermediate 3.3.1 Demonstrate the ability to work with others, present facts that support arguments, listen to dissenting points of view, and reach a shared decision. √
Commencement 3.3.1 Demonstrate leadership skills in setting goals, monitoring progress, and improving their performance. √
- Interpersonal Skills
Positive interpersonal qualities lead to teamwork and cooperation in large and small groups in family, social, and work situations.
Intermediate 3.4.1 Demonstrate the ability to work with others, present facts that support arguments, listen to dissenting points of view, and reach a shared decision. √
Commencement 3.4.1 Communicate effectively and help others to learn a new skill. √
- Technology
Technology is the process and product of human skill and ingenuity in designing and creating things from available resources to satisfy personal and societal needs and wants.
Intermediate 3.5.1 Select and use appropriate technology to complete a task. √
Commencement 3.5.1 Apply their knowledge of technology to identify and solve problems. √
- Managing Information
Information management focuses on the ability to access and use information obtained from other people, community resources, and computer networks.Intermediate 3.6.1 Select and communicate information in an appropriate format (e.g., oral, written, graphic, pictorial, multimedia). √
Commencement 3.6.1 Use technology to acquire, organize, and communicate information by entering, modifying, retrieving, and storing data. √
- Managing Resources
Using resources includes the application of financial and human factors, and the elements of time and materials to successfully carry out a planned activity.
Intermediate 3.7.1 Understand the material, human, and financial resources needed to accomplish tasks and activities. √
Commencement 3.7.1 Allocate resources to complete a task. √
- Basic skills
- Standard 3b:
Career Majors Students who choose a career major will acquire the career-specific technical knowledge/skills necessary to progress toward gainful employment, career advancement, and success in postsecondary programs.>
Essential Questions
| Who am I as a citizen? | Students develop self-management skills for researching a topic. Students develop critical thinking skills. Students develop effective interpersonal skills. | √ |
| How are my school experiences connected to my future success? | Students will acquire skills in decision making, communication, and teamwork. Students will learn various management skills. Students will participate in a simulated work environment. | √ |
| How are my social skills related to my future success? | Students will predict future situations. Students will work as a team to complete a project. Students will develop problem-solving strategies. Students will interact effectively with team partners. | √ |
| How do I develop the skills and abilities that I need to be successful in a career? How do I find out what I want to know? | Students will research topics using the internet | √ |
| Why do the choices I make now matter to my future? | Students will gain an awareness of the importance of personal responsibility and good work habits. Students will gain an awareness of the impact of their actions and choices. | √ |
Extruding
TinkerCad
- If you don't have Inkscape, download and install it from here. Otherwise open the application.
- Create a New Document. CTRL+N
- Use the available tools to create your image.
- Save the Drawing as an SVG
- Open a webGL enabled browser like Google Chrome or Firefox
- Navigate to tinkercad.com
- Once you have signed in or created a new account, click the button to design a new thing:
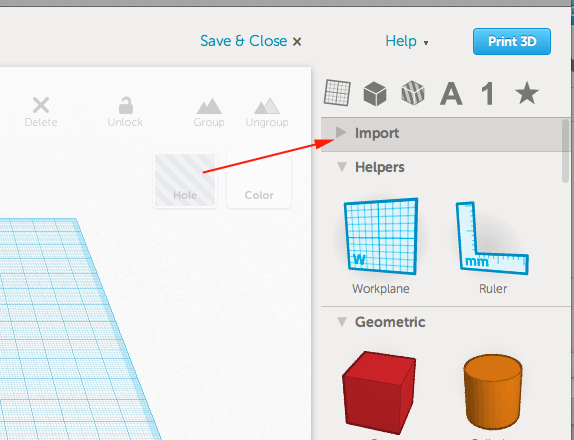
- Instead of dragging a shape on to the work plane, toggle open the import menu:
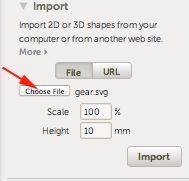
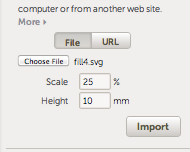
- Select File press Choose File, set the scale and height and then click on the Import button:
Blender
Blender provides a very simple way to extrude SVG files. This is great for whenever you want to convert 2D to 3D.- If you don't have Inkscape, download and install it from here. Otherwise open the application.
- Create a New Document. CTRL+N
- Use the available tools to create your image.
- Save the Drawing as an SVG


- If you don't have Blender installed, download it from blender.org and install it.
- Open Blender
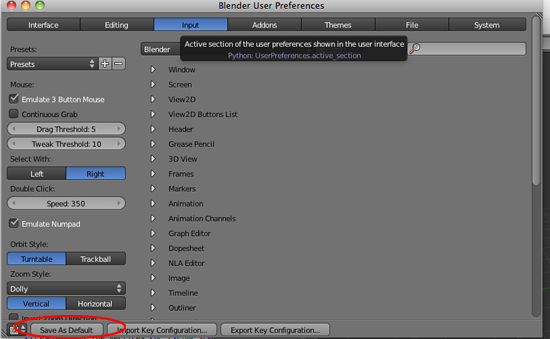
- If you have never used Blender before navigate to File>User Preferences or type (CMD+,).
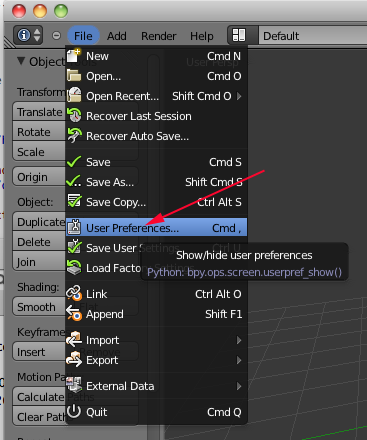
- Click on Input
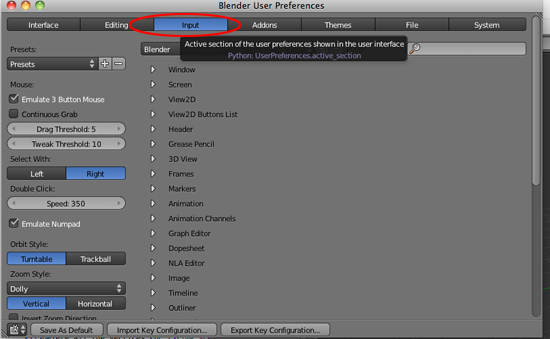
- Click on Emulate Button Mouse and Emulate Numpad
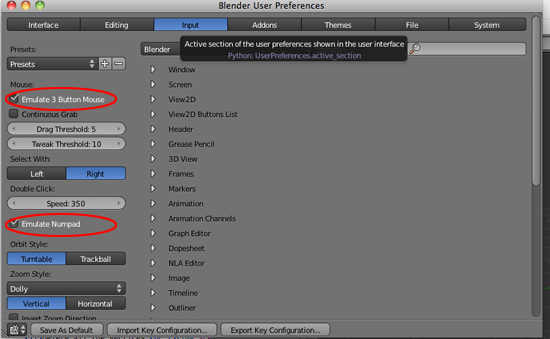
- Click on Save As Default
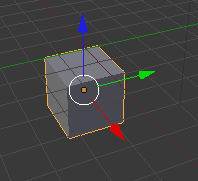
- If the cube is not selected (if there is not an orange line around it), RIGHT click on it to select it:
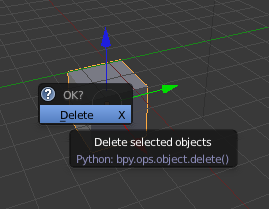
- Press X and click on Delete to delete the cube.
- Click on File>Import>Scalable Vector Graphic (.svg) and navigate to your .svg file and click on Import .SVG button in the top right corner.
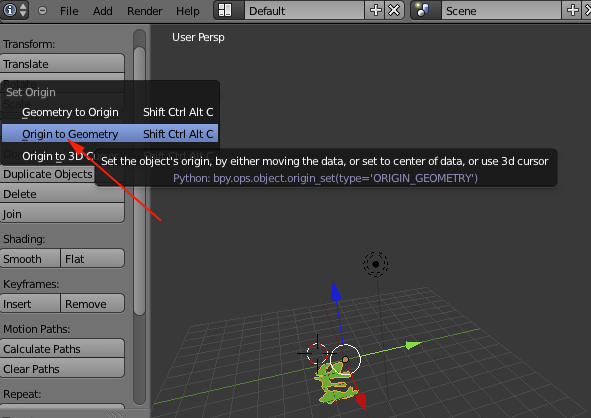
- RIGHT+click on the imported file so that it is selected.
- In the left panel select Origin to Geometry
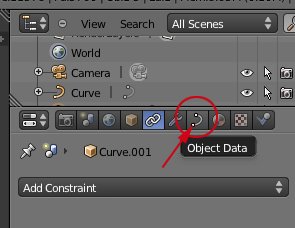
- Click on Object Data in the Right Panel:
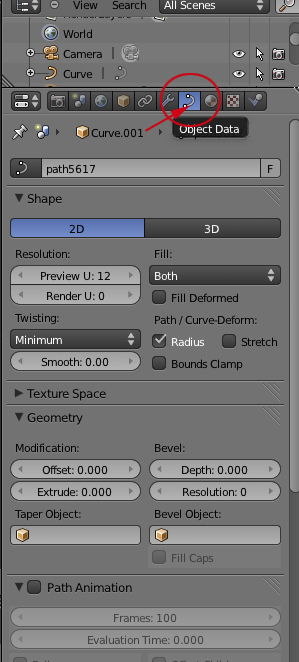
- This will open the Object Data panel:
- If it isn't open, toggle open the Geometry panel
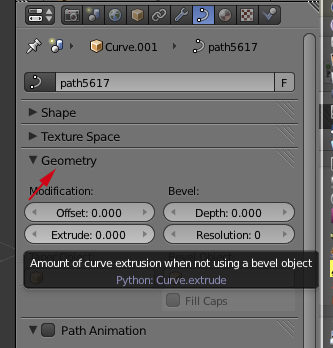
- CTRL+click on Extrude
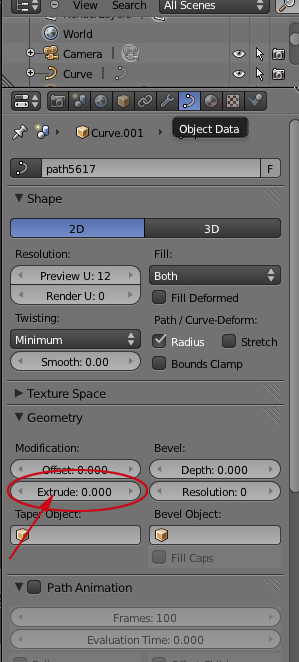
- Change the extrude value to 1
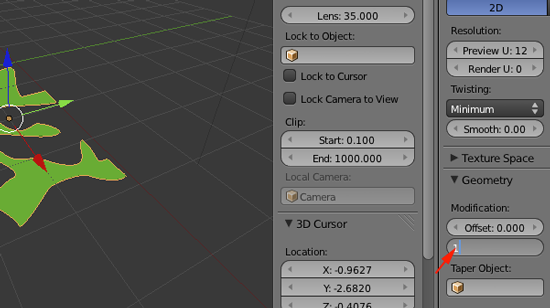
- In the Viewport press N. And resize your shape by pressing S and scaling up so that your width matches your your width from the original .svg file:
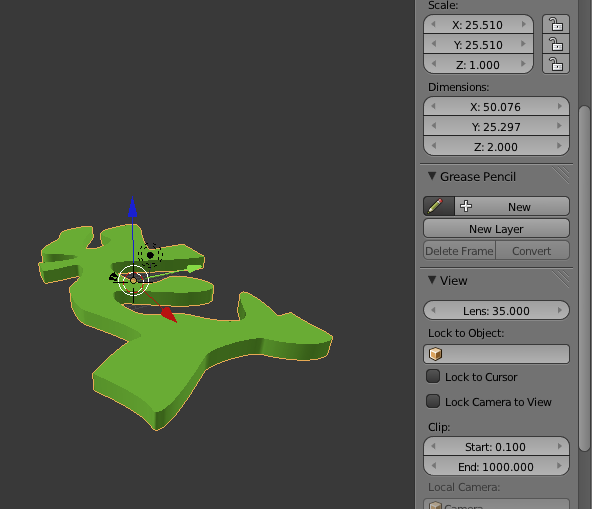
- Set the z to however high you want your tile.
- Convert the shape to a mesh by selecting Object>Convert To>Mesh from Curve
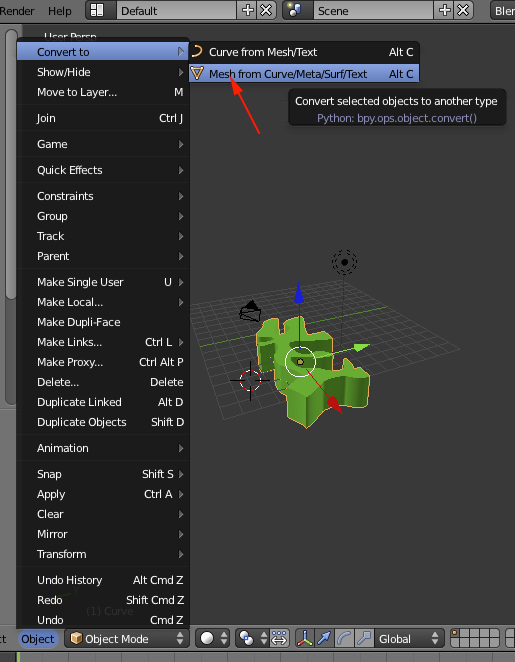
- Select the object if it is not selected and select File>Export>STL(.stl)
OmNomNom Creator
OmNomNom Creator is an application for the Mac that allows you to automatically generate 2D drawings into 3D objects. The application was created by Thingiverse user Jetty.To use the application, just drag and drop any common image format (gif, jpg, png, tiff etc.) into OmNomNom and choose the output format you want, and it will export an STL file for 3D printing. It requires OpenSCAD 2011.12 or later version to be installed.
You can use OmNomNom Creator to create 3D Cookie Cutters, Medallions, Logos, Surface Maps, Mazes, QR Codes, Stamps, or for anything where you need to get a 2D image into a 3D project.
/*assignment part 2*/
