Tessellations
Introduction
- Downlaod PolygonHelper.air
- Move the program into your Applications folder, then run it. This program will allow you to add points to easily create polygons in Openscad. The one downside is that there is no undo, so go slow.
- Click on Add point mode. When you draw out your polygon think about a square. Whatever you remove from one side gets added to the other:
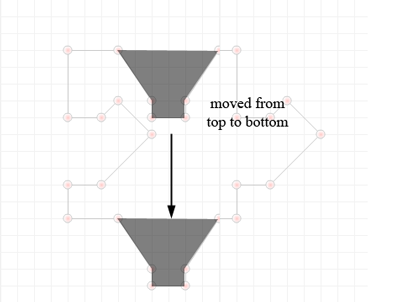
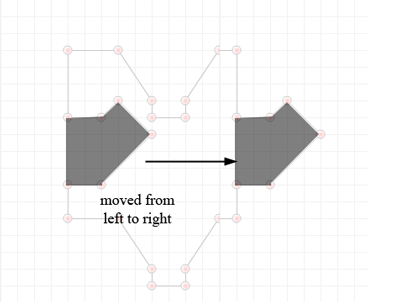
- Add points to the top of your polygon. Keep track of the overall length as your side must have the same dimension:
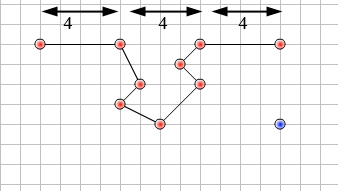
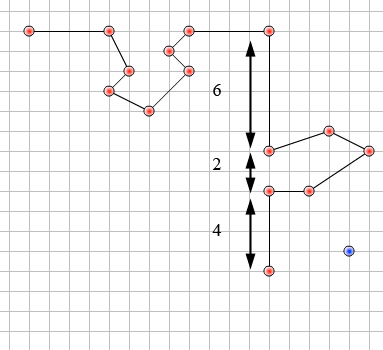
- Create the bottom. Remember to look at the shape removed from the top and add it to the bottom
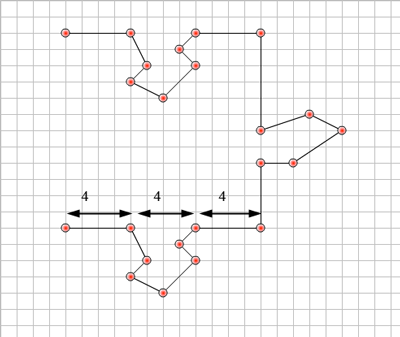
- Complete the last side
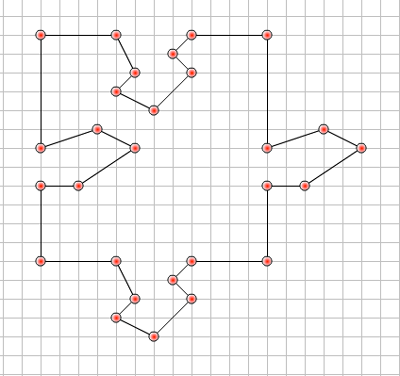
- Click on the save button. The file will be saved in a scad folder in documents.
- Double click on the file. It should open in scad. Press F5 to see your shape
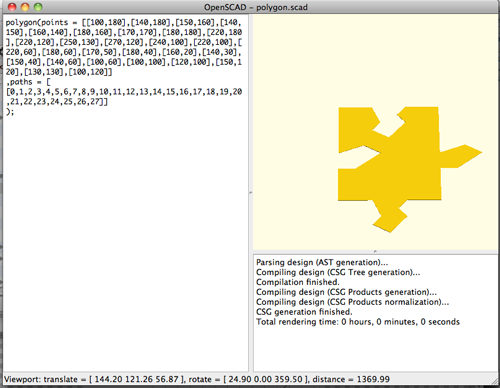
- Add a command for linear_extrude(height=__)
-
Modify the code so that the protrusions are .25mm-.5 smaller on each side.
You might want to create a setup like this, just to test your numbers
 Here is my modified code:
Here is my modified code:
module tile(){ linear_extrude(height=20) polygon(points=[ [100,179], [139,179], [148,160], [138,149], [161,139], [181,160], [171,170], [181,179], [220,179], [220,118], [250,128.5], [268,119], [239,100], [220,100], [220,60], [178,60], [167,50], [178,40], [160,22], [141,30], [151,40], [142,60], [100,60], [100,98], [121,98.5], [151,119], [129,131], [100,121]], paths=[[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]]); } scale(.25){ translate([-100,-100,-0]) tile(); color([1,0,0]) translate([-100,-220,0]) tile(); color([1,0,1]) translate([-221,-100,0]) tile(); color([0,0,1]) translate([-221,-220,0]) tile();} - Save, render, export, print
New York State Learning Standards
Mathematics, Science, and Technology
-
STANDARD 1
Analysis, Inquiry, and Design: MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS
Key Idea 1: details
Abstraction and symbolic representation are used to communicate mathematically.Elementary M1.1 Use special mathematical notation and symbolism to communicate in mathematics and to compare and describe quantities, express relationships, and relate mathematics to their immediate environment. M1.1a Use plus, minus, greater than, less than, equal to, multiplication, and division signs M1.1b Select the appropriate operation to solve mathematical problems M1.1c Apply mathematical skills to describe the natural world
Intermediate M1.1 Extend mathematical notation and symbolism to include variables and algebraic expressions in order to describe and compare quantities and express mathematical relationships. M1.1a Identify independent and dependent variables M1.1b Identify relationships among variables including: direct, indirect, cyclic, constant; identify non-related material M1.1c Apply mathematical equations to describe relationships among variables in the natural world
Physics M1.1 Use algebraic and geometric representations to describe and compare data. M1.1a Use scaled diagrams to represent and manipulate vector quantities M1.1b Represent physical quantities in graphical form M1.1c Construct graphs of real-world data (scatterplots,line or curve of best fit) M1.1d Manipulate equations to solve for unknowns M1.1e Use dimensional analysis to confirm algebraic solutions -
STANDARD 1
Analysis, Inquiry, and Design: MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS
Key Idea 3:details
Critical thinking skills are used in the solution of mathematical problems.Elementary M3.1 Explore and solve problems generated from school, home, and community situations, using concrete objects or manipulative materials when possible. √ M3.1a Use appropriate scientific tools, such as metric rulers, spring scale, pan balance, graph paper, thermometers [Fahrenheit and Celsius], graduated cylinder to solve problems about the natural world √
Intermediate M3.1 Apply algebraic and geometric concepts and skills to the solution of problems. M3.1a Explain the physical relevance of properties of a graphical representation of real-world data, e.g., slope, intercepts, area under the curve
Physics M3.1 Apply mathematical knowledge to solve real-world problems and problems that arise from the investigation of mathematical ideas, using representations such as pictures, charts, and tables. M3.1a Use appropriate scientific tools to solve problems about the natural world. √ -
STANDARD 1
Analysis, Inquiry, and Design: ENGINEERING DESIGN
Key Idea 1: details
Engineering design is an iterative process involving modeling and optimization (finding the best solution within given constraints); this process is used to develop technological solutions to problems within given constraints. (Note: The design process could apply to activities from simple investigations to long-term projects.)Elementary 1.1 Describe objects, imaginary or real, that might be modeled or made differently and suggest ways in which the objects can be changed, fixed, or improved 1.2 Investigate prior solutions and ideas from books, magazines, family, friends, neighbors, and community members 1.3 Generate ideas for possible solutions, individually and through group activity; apply age-appropriate mathematics and science skills; evaluate the ideas and determine the best solution; and explain reasons for the choices 1.4 Plan and build, under supervision, a model of the solution using familiar materials, processes, and hand tools 1.5 Discuss how best to test the solution; perform the test under teacher supervision; record and portray results through numerical and graphic means; discuss orally why things worked or didn't work; and summarize results in writing, suggesting ways to make the solution better
Intermediate T1.1 Identify needs and opportunities for technical solutions from an investigation of situations of general or social interest. T1.1a Identify a scientific or human need that is subject to a technological solution which applies scientific principles √ T1.2 Locate and utilize a range of printed, electronic, and human information resources to obtain ideas. √ T1.2a Use all available information systems for a preliminary search that addresses the need. √ T1.3 Consider constraints and generate several ideas for alternative solutions, using group and individual ideation techniques (group discussion, brainstorming, forced connections, role play); defer judgment until a number of ideas have been generated; evaluate (critique) ideas; and explain why the chosen solution is optimal. √ T1.3a Generate ideas for alternative solutions √ T1.3b Evaluate alternatives based on the constraints of design √ T1.4 Develop plans, including drawings with measurements and details of construction, and construct a model of the solution, exhibiting a degree of craftsmanship. √ T1.4a Design and construct a model of the product or process √ T1.4b Construct a model of the product or process √ T1.5 In a group setting, test their solution against design specifications, present and evaluate results, describe how the solution might have been modified for different or better results, and discuss trade-offs that might have to be made. √ T1.5a Test a design √ T1.5b Evaluate a design √
Commencement 1.1 Initiate and carry out a thorough investigation of an unfamiliar situation and identify needs and opportunities for technological invention or innovation 1.2 identify, locate, and use a wide range of information resources including subject experts, library references, magazines, videotapes, films, electronic data bases and online services, and discuss and document through notes and sketches how findings relate to the problem 1.3 generate creative solution ideas, break ideas into the significant functional elements, and explore possible refinements; predict possible outcomes using mathematical and functional modeling techniques; choose the optimal solution to the problem, clearly documenting ideas against design criteria and constraints; and explain how human values, economics, ergonomics, and environmental considerations have influenced the solution 1.4 develop work schedules and plans which include optimal use and cost of materials, processes, time, and expertise; construct a model of the solution, incorporating developmental modifications while working to a high degree of quality (craftsmanship) 1.5 in a group setting, devise a test of the solution relative to the design criteria and perform the test; record, portray, and logically evaluate performance test results through quanitative, graphic, and verbal means; and use a variety of creative verbal and graphic techniques effectively and persuasively to present conclusions, predict impacts and new problems, and suggest and pursue modifications -
STANDARD 2
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Key Idea 1: details
Information technology is used to retrieve, process, and communicate information as a tool to enhance learning.Elementary 1.1 Use computer technology,traditional paper-based resources,and interpersonal discussions to learn, do, and share science in the classroom √ 1.2 Select appropriate hardware and software that aids in wordprocessing, creating databases, telecommunications, graphing, data display, and other tasks √ 1.3 Use information technology to link the classroom to world events
Intermediate 1.1 Use a range of equipment and software to integrate several forms of information in order to create good-quality audio, video, graphic, and text-based presentations. 1.2 Use spreadsheets and database software to collect, process, display, and analyze information. Students access needed information from electronic databases and on-line telecommunication services. 1.3 Systematically obtain accurate and relevant information pertaining to a particular topic from a range of sources, including local and national media, libraries, muse- ums, governmental agencies, industries, and individuals. 1.4 Collect data from probes to measure events and phenomena. 1.4a Collect the data, using the appropriate, available tool 1.4b Organize the data 1.4c Use the collected data to communicate a scientific concept √ 1.5 Use simple modeling programs to make predictions.
Physics 1.1 Understand and use the more advanced features of word processing, spreadsheets, and database software. 1.2 Prepare multimedia presentations demonstrating a clear sense of audience and purpose. (Note: Multimedia may include posters, slides, images, presentation software, etc.) √ 1.2a Extend knowledge of physical phenomena through independent investigation, e.g., literature review, electronic resources, library research 1.2b Use appropriate technology to gather experimental data, develop models,and present results √ 1.3 Access, select, collate, and analyze information obtained from a wide range of sources such as research databases, foundations, organizations, national libraries, and electronic communication networks, including the Internet. 1.3a Use knowledge of physics to evaluate articles in the popular press on contemporary scientific topics 1.4 Utilize electronic networks to share information. √ 1.5 Model solutions to a range of problems in mathematics, science, and technology, using computer simulation software. √ 1.5a Use software to model and extend classroom and laboratory experiences,recognizing the differences between the model used for understanding and real-world behavior √ -
STANDARD 3
Strand: Problem Solving
details
- Understand numbers, multiple ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems;
- Understand meanings of operations and procedures, and how they relate to one another;
- compute accurately and make reasonable estimates.
Fifth, Sixth Grade 1.1 Know the difference between relevant and irrelevant information when solving problems √ 1.2 Understand that some ways of representing a problem are more helpful than others √ 1.3 Interpret information correctly, identify the problem, and generate possible solutions √ 1.4 Act out or model with manipulatives activities involving mathematical content from literature √ 1.5 Formulate problems and solutions from everyday situations √
Seventh, Eighth Grade 1.1 Use a variety of strategies to understand new mathematical content and to develop more efficient methods √ 1.2 Construct appropriate extensions to problem situations √ 1.3 Understand and demonstrate how written symbols represent mathematical ideas 1.4 Observe patterns and formulate generalizations 1.5 Make conjectures from generalizations 1.6 Represent problem situations verbally, numerically, algebraically, and graphically 1.7 Understand that there is no one right way to solve mathematical problems but that different methods have advantages and disadvantages √ 1.8 Understand how to break a complex problem into simpler parts or use a similar problem type to solve a problem √ 1.9 Work backwards from a solution √ 1.10 Use proportionality to model problems 1.11 Work in collaboration with others to solve problems √ 1.12 Interpret solutions within the given constraints of a problem √ 1.13 Set expectations and limits for possible solutions √ 1.14 Determine information required to solve the problem √ 1.15 Choose methods for obtaining required information √ 1.16 Justify solution methods through logical argument 1.17 Evaluate the efficiency of different representations of a problem 1.18 Determine the efficiency of different representations of a problem
Integrated Algebra 1.1 Use a variety of problem solving strategies to understand new mathematical content 1.2 Recognize and understand equivalent representations of a problem situation or a mathematical concept 1.3 Observe and explain patterns to formulate generalizations and conjectures 1.4 Use multiple representations to represent and explain problem situations (e.g., verbally, numerically, algebraically, graphically) 1.5 Choose an effective approach to solve a problem from a variety of strategies (numeric, graphic, algebraic) 1.6 Use a variety of strategies to extend solution methods to other problems 1.7 Work in collaboration with others to propose, critique, evaluate, and value alternative approaches to problem solving √ 1.8 Determine information required to solve a problem, choose methods for obtaining the information, and define parameters for acceptable solutions √ 1.9 Interpret solutions within the given constraints of a problem √ 1.10 Evaluate the relative efficiency of different representations and solution methods of a problem √
Geometry 1.1 Use a variety of problem solving strategies to understand new mathematical content √ 1.2 Observe and explain patterns to formulate generalizations and conjectures 1.3 Use multiple representations to represent and explain problem situations (e.g., spatial, geometric, verbal, numeric, algebraic, and graphical representations) 1.4 Construct various types of reasoning, arguments, justifications and methods of proof for problems 1.5 Choose an effective approach to solve a problem from a variety of strategies (numeric, graphic, algebraic) 1.6 Use a variety of strategies to extend solution methods to other problems 1.7 Work in collaboration with others to propose, critique, evaluate, and value alternative approaches to problem solving √ 1.8 Determine information required to solve a problem, choose methods for obtaining the information, and define parameters for acceptable solutions √ 1.9 Interpret solutions within the given constraints of a problem √ 1.10 Evaluate the relative efficiency of different representations and solution methods of a problem
Algebra 2 and Trigonometry 1.1 Use a variety of problem solving strategies to understand new mathematical content √ 1.2 Recognize and understand equivalent representations of a problem situation or a mathematical concept 1.3 Observe and explain patterns to formulate generalizations and conjectures 1.4 Use multiple representations to represent and explain problem situations (e.g., verbally, numerically, algebraically, graphically) 1.5 Choose an effective approach to solve a problem from a variety of strategies (numeric, graphic, algebraic) 1.6 Use a variety of strategies to extend solution methods to other problems 1.7 Work in collaboration with others to propose, critique, evaluate, and value alternative approaches to problem solving √ 1.8 Determine information required to solve a problem, choose methods for obtaining the information, and define parameters for acceptable solutions √ 1.9 Interpret solutions within the given constraints of a problem √ 1.10 Evaluate the relative efficiency of different representations and solution methods of a problem
- Understand numbers, multiple ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems;
-
STANDARD 3
Strand: Connections
details
- Recognize and use connections among mathematical ideas;
- Understand how mathematical ideas interconnect and build on one another to
produce a coherent whole;
- Recognize and apply mathematics in contexts outside of mathematics.
Fifth, Sixth Grade 4.1 Understand and make connections and conjectures in their everyday experiences to mathematical ideas √ 4.2 Explore and explain the relationship between mathematical ideas 4.3 Connect and apply mathematical information to solve problems √ 4.4 Understand multiple representations and how they are related 4.5 Model situations with objects and representations and be able to draw conclusions √ 4.6 Recognize the presence of mathematics in their daily lives √ 4.7 Apply mathematics to solve problems that develop outside of mathematics √ 4.8 Investigate the presence of mathematics in careers and areas of interest √ 4.9 Recognize and apply mathematics to other disciplines and areas of interest √
Seventh, Eighth Grade 4.1 Understand and make connections among multiple representations of the same mathematical idea 4.2 Recognize connections between subsets of mathematical ideas 4.3 Connect and apply mathematical information to solve problems √ 4.4 Model situations mathematically, using representations to draw conclusions and formulate new situations 4.5 Understand how concepts, procedures, and mathematical results in one area of mathematics can be used to solve problems in other areas of mathematics 4.6 Recognize the presence of mathematics in their daily lives √ 4.7 Apply mathematics to solve problems that develop outside of mathematics √ 4.8 Investigate the presence of mathematics in careers and areas of interest √ 4.9 Recognize and apply mathematics to other disciplines and areas of interest √
Integrated Algebra, Geometry, Algebra 2 and Trigonometry 4.1 Understand and make connections among multiple representations of the same mathematical idea 4.2 Understand the corresponding procedures for similar problems or mathematical concepts 4.3 Model situations mathematically, using representations to draw conclusions and formulate new situations 4.4 Understand how concepts, procedures, and mathematical results in one area of mathematics can be used to solve problems in other areas of mathematics 4.5 Understand how quantitative models connect to various physical models and representations √ 4.6 Recognize and apply mathematics to situations in the outside world √ 4.7 Recognize and apply mathematical ideas to problem situations that develop outside of mathematics √ 4.8 Develop an appreciation for the historical development of mathematics
- Recognize and use connections among mathematical ideas;
-
STANDARD 3
Strand: Representation
details
- Create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical ideas;
- Select, apply, and translate among mathematical representations to solve problems;
- Use representations to model and interpret physical, social, and mathematical phenomena.
Fifth, Sixth Grade 5.1 Use physical objects, drawings, charts, tables, graphs, symbols, equations, or objects created using technology as representations √ 5.2 Explain, describe, and defend mathematical ideas using representations 5.3 Read, interpret, and extend external models 5.4 Use standard and nonstandard representations with accuracy and detail 5.5 Use representations to explore problem situations √ 5.6 Investigate relationships between different representations and their impact on a given problem 5.7 Use mathematics to show and understand physical phenomena (e.g., determine the perimeter of a bulletin board) √ 5.8 Use mathematics to show and understand social phenomena (e.g., construct tables to organize data showing book sales) 5.9 Use mathematics to show and understand mathematical phenomena (e.g., find the missing value that makes the equation true: (3 + 4) + 5 = 3 + (4 + ___ )
Seventh, Eighth Grade 5.1 Use physical objects, drawings, charts, tables, graphs, symbols, equations, or objects created using technology as representations √ 5.2 Explain, describe, and defend mathematical ideas using representations 5.3 Recognize, compare, and use an array of representational forms 5.4 Explain how different representations express the same relationship 5.5 Use standard and non-standard representations with accuracy and detail 5.6 Use representations to explore problem situations 5.7 Investigate relationships between different representations and their impact on a given problem 5.8 Use representation as a tool for exploring and understanding mathematical ideas 5.9 Use mathematics to show and understand physical phenomena (e.g., make and interpret scale drawings of figures or scale models of objects) √ 5.10 Use mathematics to show and understand social phenomena (e.g., determine profit from sale of yearbooks) 5.11 Use mathematics to show and understand mathematical phenomena (e.g., use tables, graphs, and equations to show a pattern underlying a function)
Integrated Algebra 5.1 Use physical objects, diagrams, charts, tables, graphs, symbols, equations, or objects created using technology as representations of mathematical concepts √ 5.2 Recognize, compare, and use an array of representational forms 5.3 Use representation as a tool for exploring and understanding mathematical ideas 5.4 Select appropriate representations to solve problem situations 5.5 Investigate relationships between different representations and their impact on a given problem 5.6 Use mathematics to show and understand physical phenomena (e.g., find the height of a building if a ladder of a given length forms a given angle of elevation with the ground) √ 5.7 Use mathematics to show and understand social phenomena (e.g., determine profit from student and adult ticket sales) 5.8 Use mathematics to show and understand mathematical phenomena (e.g., compare the graphs of the functions represented by the equations y = x2 and y = −x2 )
Geometry 5.1 Use physical objects, diagrams, charts, tables, graphs, symbols, equations, or objects created using technology as representations of mathematical concepts √ 5.2 Recognize, compare, and use an array of representational forms 5.3 Use representation as a tool for exploring and understanding mathematical ideas 5.4 Select appropriate representations to solve problem situations 5.5 Investigate relationships between different representations and their impact on a given problem 5.6 Use mathematics to show and understand physical phenomena (e.g., determine the number of gallons of water in a fish tank) √ 5.7 Use mathematics to show and understand social phenomena (e.g., determine if conclusions from another person's argument have a logical foundation) 5.8 Use mathematics to show and understand mathematical phenomena (e.g., use investigation, discovery, conjecture, reasoning, arguments, justification and proofs to validate that the two base angles of an isosceles triangle are congruent)
Algebra 2 and Trigonometry 5.1 Use physical objects, diagrams, charts, tables, graphs, symbols, equations, or objects created using technology as representations of mathematical concepts √ 5.2 Recognize, compare, and use an array of representational forms 5.3 Use representation as a tool for exploring and understanding mathematical ideas 5.4 Select appropriate representations to solve problem situations 5.5 Investigate relationships between different representations and their impact on a given problem 5.6 Use mathematics to show and understand physical phenomena (e.g., determine the number of gallons of water in a fish tank) √ 5.7 Use mathematics to show and understand social phenomena (e.g., interpret the results of an opinion poll) 5.8 Use mathematics to show and understand mathematical phenomena (e.g., use random number generator to simulate a coin toss)
- Create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical ideas;
-
STANDARD 4
Process Skills Electricity and Magnetism:
details
Physics Measure current and voltage in a circuit √ Use measurements to determine the resistance of a circuit element √ Interpret graphs of voltage versus current Measure and compare the resistance of conductors of various lengths and cross-sectional areas Construct simple series and parallel circuits √ Draw and interpret circuit diagrams which include voltmeters and ammeters √ Predict the behavior of lightbulbs in series and parallel circuits Map the magnetic field of a permanent magnet, indicating the direction of the field between the N (north-seeking) and S (south-seeking) poles -
STANDARD 5
Technology: Engineering Design
(See Standard 1:ENGINEERING DESIGN)
Key Idea 1:
Engineering design is an iterative process involving modeling and optimization used to develop technological solutions to problems within given constraints. -
STANDARD 5
Technology: Engineering Design
Key Idea 2: details
Technological tools, materials, and other resources should be selected on the basis of safety, cost, availability, appropriateness, and environmental impact; technological processes change energy, information, and material resources into more useful forms.Elementary 2.1 Explore, use, and process a variety of materials and energy sources to design and construct things. √ 2.2 Understand the importance of safety, cost, ease of use, and availability in selecting tools and resources for a specific purpose. 2.3 Develop basic skill in the use of hand tools 2.4 Use simple manufacturing processes (e.g., assembly, multiple stages of production, quality control) to produce a product √ 2.5 Use appropriate graphic and electronic tools and techniques to process information. √
Intermediate 2.1 Choose and use resources for a particular purpose based upon an analysis and understanding of their properties, costs, availability, and environmental impact √ 2.2 Use a variety of hand tools and machines to change materials into new forms through forming, separating, and combining processes, and processes which cause internal change to occur √ 2.3 Combine manufacturing processes with other technological processes to produce, market, and distribute a product 2.4 Process energy into other forms and information into more meaningful information.
Commencement 2.1 Test, use, and describe the attributes of a range of material (including synthetic and composite materials), information, and energy resources √ 2.2 Select appropriate tools, instruments, and equipment and use them correctly to process materials, energy, and information √ 2.3 Explain tradeoffs made in selecting alternative resources in terms of safety, cost, properties, availability, ease of processing, and disposability 2.4 Describe and model methods (including computer-based methods) to control system processes and monitor system outputs √ -
STANDARD 5
Technology: Computer Technology
Key Idea 3: details
Computers, as tools for design, modeling, information processing, communication, and system control, have greatly increased human productivity and knowledge.Elementary 3.1 Identify and describe the function of the major components of a computer system. 3.2 Use the computer as a tool for generating and drawing ideas. √ 3.3 Control computerized devices and systems through programming. √ 3.4 Model and simulate the design of a complex environment by giving direct commands. √
Intermediate 3.1 Assemble a computer system including keyboard, central processing unit and disc drives, mouse, modem, printer, and monitor 3.2 Use a computer system to connect to and access needed information from various Internet sites √ 3.3 Use computer hardware and software to draw and dimension prototypical designs √ 3.4 Use a computer as a modeling tool √ 3.5 Use a computer system to monitor and control external events and/or systems √
Commencement 3.1 Understand basic computer architecture and describe the function of computer subsystems and peripheral devices 3.2 Select a computer system that meets personal needs 3.3 Attach a modem to a computer system and telephone line, set up and use communications software, connect to various online networks, including the Internet, and access needed information using email, telnet, gopher, ftp, and web searches √ 3.4 Use computer-aided drawing and design (CADD) software to model realistic solutions to design problems √ 3.5 Develop an understanding of computer programming and attain some facility in writing computer programs √ -
STANDARD 5
Technology: Technological Systems
Key Idea 4: details
Technological systems are designed to achieve specific results and produce outputs, such as products, structures, services, energy, or other systems.Elementary 4.1 Identify familiar examples of technological systems that are used to satisfy human needs and wants, and select them on the basis of safety, cost, and function. 4.2 Assemble and operate simple technological systems, including those with interconnecting mechanisms to achieve different kinds of movement. 4.3 Understand that larger systems are made up of smaller component subsystems.
Intermediate 4.1 Select appropriate technological systems on the basis of safety, function, cost, ease of operation, and quality of post-purchase support 4.2 Assemble, operate, and explain the operation of simple open- and closed-loop electrical, electronic, mechanical, and pneumatic systems 4.3 Describe how subsystems and system elements (inputs, processes, outputs) interact within systems 4.4 Describe how system control requires sensing information, processing it, and making changes √
Commencement 4.1 Explain why making tradeoffs among characteristics, such as safety, function, cost, ease of operation, quality of post-purchase support, and environmental impact, is necessary when selecting systems for specific purposes 4.2 Model, explain, and analyze the performance of a feedback control system 4.3 Explain how complex technological systems involve the confluence of numerous other systems -
STANDARD 6
Interconnectedness: Common Themes SYSTEMS THINKING:
Key Idea 1: details
Through systems thinking, people can recognize the commonalities that exist among all systems and how parts of a system interrelate and combine to perform specific functions.Elementary 1.1 Observe and describe interactions among components of simple systems. √ 1.2 Identify common things that can be considered to be systems (e.g., a plant population, a subway system, human beings).
Intermediate 1.1 Describe the differences between dynamic systems and organizational systems. 1.2 describe the differences and similarities between engineering systems, natural systems, and social systems. 1.3 Describe the differences between open- and closed-loop systems. 1.4 Describe how the output from one part of a system (which can include material, energy, or information) can become the input to other parts.
Commencement 1.1 Explain how positive feedback and negative feedback have opposite effects on system outputs. 1.2 Use an input-process-output-feedback diagram to model and compare the behavior of natural and engineered systems. 1.3 Define boundary conditions when doing systems analysis to determine what influences a system and how it behaves. -
STANDARD 6
Interconnectedness: Common Themes MODELS:
Key Idea 2: details
Models are simplified representations of objects, structures, or systems used in analysis, explanation, interpretation, or design.Elementary 2.1 Analyze,construct,and operate models in order to discover attributes of the real thing √ 2.2 Discover that a model of something is different from the real thing but can be used to study the real thing √ 2.3 Use different types of models, such as graphs,sketches,diagrams,and maps,to represent various aspects of the real world
Intermediate 2.1 Select an appropriate model to begin the search for answers or solutions to a question or problem. 2.2 Use models to study processes that cannot be studied directly (e.g., when the real process is too slow, too fast, or too dangerous for direct observation). √ 2.3 Demonstrate the effectiveness of different models to represent the same thing and the same model to represent different things.
Physics 2.1 Revise a model to create a more complete or improved representation of the system. 2.2 Collect information about the behavior of a system and use modeling tools to represent the operation of the system. √ 2.2a Use observations of the behavior of a system to develop a model 2.3 Find and use mathematical models that behave in the same manner as the processes under investigation. 2.3a Represent the behavior of real-world systems,using physical and mathematical models √ 2.4 Compare predictions to actual observations, using test models. √ 2.4a Validate or reject a model based on collated experimental data √ 2.4b Predict the behavior of a system,using a model √ -
STANDARD 7
Interdisciplinary Problem Solving CONNECTIONS:
Key Idea 1:details
The knowledge and skills of mathematics, science, and technology are used together to make informed decisions and solve problems, especially those relating to issues of sci- ence/technology/society, consumer decision making, design, and inquiry into phenomena.Elementary 1.1 Analyze science/technology/society problems and issues that affect their home, school, or community, and carry out a remedial course of action 1.2 Make informed consumer decisions by applying knowledge about the attributes of particular products and making cost/benefit trade-offs to arrive at an optimal choice 1.3 Design solutions to problems involving a familiar and real context, investigate related science concepts to determine the solution, and use mathematics to model, quantify, measure, and compute √ 1.4 Observe phenomena and evaluate them scientifically and mathematically by conducting a fair test of the effect of variables and using mathematical knowledge and technological tools to collect, analyze, and present data and conclusions
Intermediate 1.1 Analyze science/technology/society problems and issues at the local level and plan and carry out a remedial course of action. 1.2 Make informed consumer decisions by seeking answers to appropriate questions about products, services, and systems; determining the cost/benefit and risk/benefit tradeoffs; and applying this knowledge to a potential purchase. 1.3 Design solutions to real-world problems of general social interest related to home, school, or community using scientific experimentation to inform the solution and applying mathematical concepts and reasoning to assist in developing a solution. √ 1.4 Describe and explain phenomena by designing and conducting investigations involving systematic observations, accurate measurements, and the identification and control of variables; by inquiring into relevant mathematical ideas; and by using mathematical and technological tools and procedures to assist in the investigation. 1.5 Analyze science/technology/society problems and issues at the local level and plan and carry out a remedial course of action.
Physics Address real-world problems,using scientific methodology -
STANDARD 7
Interdisciplinary Problem Solving STRATEGIES:
Key Idea 2: details
Solving interdisciplinary problems involves a variety of skills and strategies, including effective work habits; gathering and processing information; generating and analyzing ideas; realizing ideas; making connections among the common themes of mathematics, science, and technology; and presenting results.Physics 2.1 Collect,analyze,interpret,and present data,using appropriate tools √ 2.2 When students participate in an extended,culminating mathematics,science,and technology project, then students should: Work effectively—Contributing to the work of a brainstorming group, laboratory partnership, cooperative learning group, or project team; planning procedures; identify and managing responsibilities of team members; and staying on task, whether working alone or as part of a group. √ Gather and process information —Accessing information from printed media, electronic data bases, and community resources and using the information to develop a definition of the problem and to research possible solutions. √ Generate and analyze ideas — Developing ideas for proposed solutions, investigating ideas, collecting data, and showing relationships and patterns in the data. √ Observe common themes—Observing examples of common unifying themes, applying them to the problem, and using them to better understand the dimensions of the problem. √ Realize ideas—Constructing components or models, arriving at a solution, and evaluating the result. √ Present results—Using a variety of media to present the solution and to communicate the results. √
CDOS
- Standard 2: Integrated Learning
details
Students will demonstrate how academic knowledge and skills are applied in the workplace and other settings.
Integrated learning encourages students to use essential academic concepts, facts, and procedures in applications related to life skills and the world of work. This approach allows students to see the usefulness of the concepts that they are being asked to learn and to understand their potential application in the world of work.
Elementary 2.1 Identify academic knowledge and skills that are required in specific occupations 2.2 Demonstrate the difference between the knowledge of a skill and the ability to use the skill 2.3 Solve problems that call for applying academic knowledge and skills. √
Intermediate 2.1 Apply academic knowledge and skills using an interdisciplinary approach to demonstrate the relevance of how these skills are applied in work-related situations in local, state, national, and international communities 2.2 Solve problems that call for applying academic knowledge and skills √ 2.3 Use academic knowledge and skills in an occupational context, and demonstrate the application of these skills by using a variety of communication techniques (e.g., sign language, pictures, videos, reports, and technology).
Commencement 2.1 Demonstrate the integration and application of academic and occupational skills in their school learning, work, and personal lives. √ 2.2 Use academic knowledge and skills in an occupational context, and demonstrate the application of these skills by using a variety of communication techniques (e.g., sign language, pictures, videos, reports, and technology) √ 2.3 Research, interpret, analyze, and evaluate information and experiences as related to academic knowledge and technical skills when completing a career plan. - Standard 3a: Universal Foundation Skills
details
Students will demonstrate mastery of the foundation skills and competencies essential for success in the workplace.
- Basic skills
Basic skills include the ability to read, write, listen, and speak as well as perform arithmetical and mathematical functions.
Elementary 3.1.1 Listen to and read the ideas of others and express themselves both orally and in writing; they use basic mathematical concepts and computations to solve problems. √
Intermediate 3.1.1 Listen to and read the ideas of others and analyze what they hear and read; acquire and use information from a variety of sources; and apply a combination of mathematical operations to solve problems in oral or written form. √
Commencement 3.1.1 Use a combination of techniques to read or listen to complex information and analyze what they hear or read; convey information confidently and coherently in written or oral form; and analyze and solve mathematical problems requiring use of multiple computational skills. √ - Thinking skills
Thinking skills lead to problem solving, experimenting, and focused observation and allow the application of knowledge to new and unfamiliar situations.
Elementary 3.2.1 Use ideas and information to make decisions and solve problems related to accomplishing a task. √
Intermediate 3.2.1 Evaluate facts, solve advanced problems, and make decisions by applying logic and reasoning skills. √
Commencement 3.2.1 Demonstrate the ability to organize and process information and apply skills in new ways. √
- Personal Qualities
Personal qualities generally include competence in self-management and the ability to plan, organize, and take independent action.
Elementary 3.3.1 Demonstrate the personal qualities that lead to responsible behavior. √
Intermediate 3.3.1 Demonstrate the ability to work with others, present facts that support arguments, listen to dissenting points of view, and reach a shared decision. √
Commencement 3.3.1 Demonstrate leadership skills in setting goals, monitoring progress, and improving their performance. √
- Interpersonal Skills
Positive interpersonal qualities lead to teamwork and cooperation in large and small groups in family, social, and work situations.
Elementary 3.4.1 Relate to people of different ages and from diverse backgrounds.
Intermediate 3.4.1 Demonstrate the ability to work with others, present facts that support arguments, listen to dissenting points of view, and reach a shared decision. √
Commencement 3.4.1 Communicate effectively and help others to learn a new skill. √
- Technology
Technology is the process and product of human skill and ingenuity in designing and creating things from available resources to satisfy personal and societal needs and wants.
Elementary 3.5.1 Demonstrate an awareness of the different types of technology available to them and of how technology affects society.
Intermediate 3.5.1 Select and use appropriate technology to complete a task. √
Commencement 3.5.1 Apply their knowledge of technology to identify and solve problems. √
- Managing Information
Information management focuses on the ability to access and use information obtained from other people, community resources, and computer networks.Elementary 3.6.1 Describe the need for data and obtain data to make decisions. √
Intermediate 3.6.1 Select and communicate information in an appropriate format (e.g., oral, written, graphic, pictorial, multimedia). √
Commencement 3.6.1 Use technology to acquire, organize, and communicate information by entering, modifying, retrieving, and storing data. √
- Managing Resources
Using resources includes the application of financial and human factors, and the elements of time and materials to successfully carry out a planned activity.Elementary 3.7.1 Demonstrate an awareness of the knowledge, skills, abilities, and resources needed to complete a task. √
Intermediate 3.7.1 Understand the material, human, and financial resources needed to accomplish tasks and activities. √
Commencement 3.7.1 Allocate resources to complete a task. √
- Systems
Systems skills include the understanding of and ability to work within natural and constructed systems.Elementary 3.8.1 Demonstrate understanding of how a system operates and identify where to obtain information and resources within the system. √
Intermediate 3.8.1 Understand the process of evaluating and modifying systems within an organization. √
Commencement 3.8.1 Demonstrate an understanding of how systems performance relates to the goals, resources, and functions of an organization. √
- Basic skills
- Standard 3b: Career Majors
details
Students who choose a career major will acquire the career-specific technical knowledge/skills necessary to progress toward gainful employment, career advancement, and success in postsecondary programs.
- Engineering/Technologies
Core, Specialized and Experiential 3b.1 Foundation Development—Develop practical understanding of engineering technology through reading, writing, sample problem solving, and employment experiences. √ 3b.2 Technology—Demonstrate how all types of engineering/technical organizations, equipment (hardware/software), and well-trained human resources assist and expedite the production/distribution of goods and services 3b.3 Engineering/Industrial Processes—Demonstrate knowledge of planning, product development and utilization, and evaluation that meets the needs of industry.
- Engineering/Technologies
